Innovations in the pharmaceutical industry proved to be a tall order, as drug development’s success rate has been traditionally tremendously low. However, the COVID-19 pandemic whipped up R&D centers, markets, and leaders to develop the response to the crisis faster than ever. AI and ML bring to the table a toolbox to overcome new challenges in the whole industry. Significant that the Healthcare Artificial Intelligence market is expected to reach $51.3 billion by 2027 at CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 41.4% starting from 2020. Check out this fresh guide on the latest updates that AI and machine learning brought to the pharmaceutical market in the EU, including recent applications and the most significant challenges.
Recent AI and ML applications in healthcare and pharma proved that these technologies are reaching the ‘Slope of Enlightenment’ in the Gartner Hype Cycle. It seems like the industry has no choice at the moment. Per Subroto Mukherjee, Head of Innovation and Emerging Technology at GlaxoSmithKline, the development of the new vaccines against coronavirus would take from eight to ten years before. In contrast, the ones available now took 300 days from the start of development to the first testings. The rationale of using ML in the industry is to lower attrition and costs while increasing the success rate for new drug development.
Hence, the power of using ML algorithms to parse significant amounts of data to learn from it and make determination or prediction about the future of the new data sets come to the scene. The algorithms show higher performance with the increase of quantity and quality of data, leading to the question of data regulation, which we cover further. Data collected like images, texts, biometrics, assay, and other information from wearables stand as the field for developing the new models or formulas that are still unknown but could bring crucial changes. Practically there has been next proven applications of AI and ML in the market:
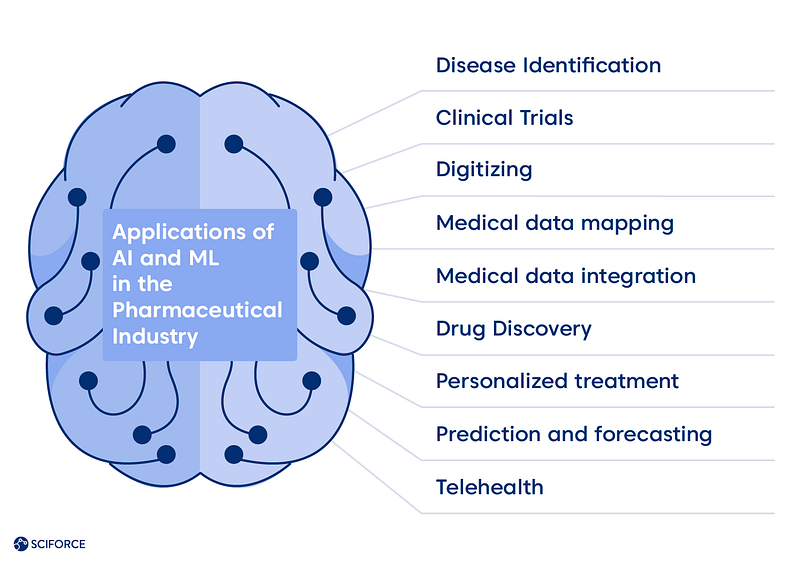
To illustrate the mentioned applications, see how the European companies resolve the scientific problems delivering faster pharmaceutical, bispecific target diseases treatments, and rare disease patients treatment matching using machine learning. The UK and France-based companies are on our list this time.
Tessella is a data science consultancy offering AI and data science services by building machine learning models. They claim to have helped GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) improve the salt and polymorph screening process of the drugs’ development. It helps to find the best physical form of the new drug substance. The company developed an ML model that automates medicine preparation processes like liquid addition and mixing, heating and cooling, shaking, sample transfer, and solid dispensing.
Healx has developed HealNet, software helping in matching rare disease patients with appropriate drug treatments. Their ML algorithms are built on a database consisting of publicly available data and specific sources, including clinical trials, symptoms data, chemical structure, drug targets, patents, and scientific literature.
Exscientia claims their software can discover small molecules and compounds treating bispecific target diseases. This solution is using an ML model that predicts the specific development of the bispecific diseases.
Owkin claims their solution, Socrates database helps in creating predictive models for drug development optimization.
GlaxoSmithKline, a UK-based multinational company, applied the ML in predictive forecasting for some popular seasonal brands. It helps to foresee the possible peaks and troughs of coming cold and flu or allergy in a specific region, assisting local authorities to deliver an effective health communications campaign.
Statistical technology depends on the data quality to generate meaningful and impactful results. Hence, pharmaceutical and healthcare companies should balance the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), starting from 2018. It is also still applicable to the UK, which is leaving the EU. The data, which is under GDPR patient’s consent, includes the following categories:
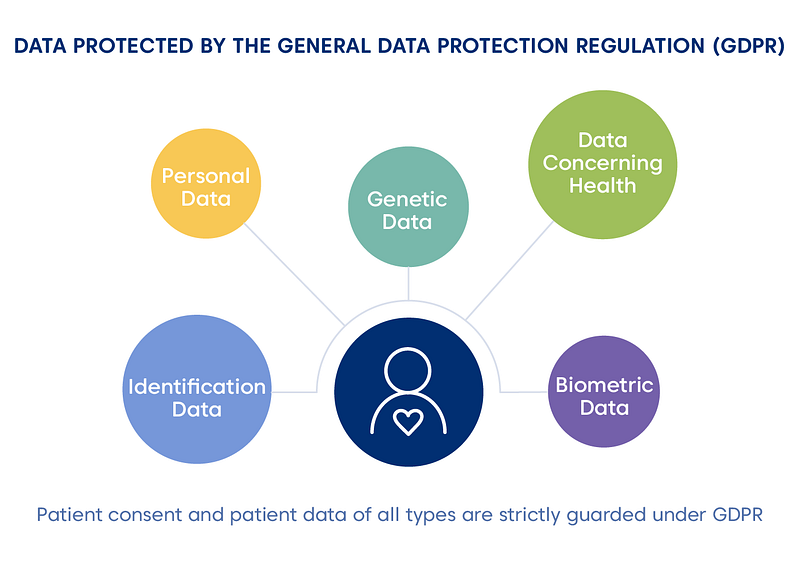
These regulations hold the extraterritorial reach, which means that any global business dealing with EU customers should consider this aspect. Noncompliance to the GDPR leads to 4% of annual global revenue or €20 million fine. It does not sound inspirational, is it?
Per David Champagne, a member of the McKinsey Digital Practice, et al. in their article devoted to realizing machine learning potential, there is a way to escape a bottleneck. Pharmaceutical companies can move through the regulatory landscape effectively. In the meantime, all the actors should consider these points:
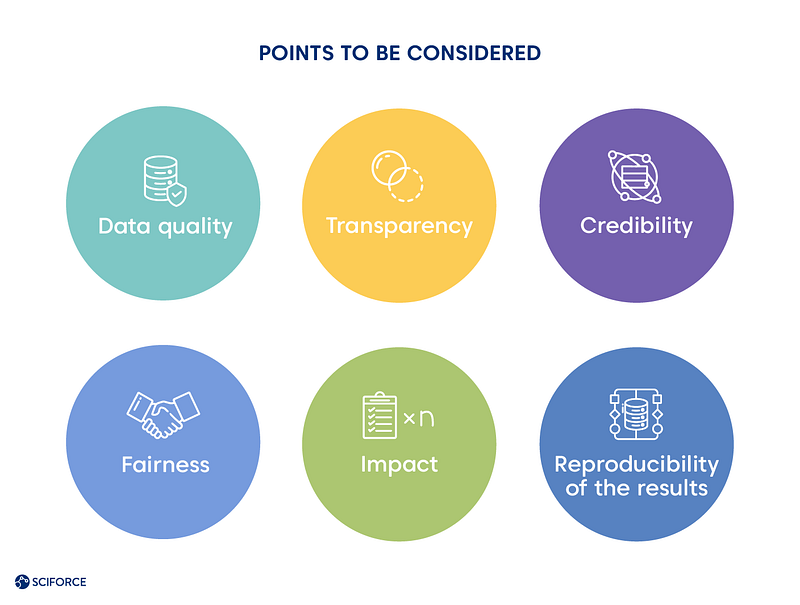
Recent studies worldwide are experimenting with AI and ML techniques for decision-making in treatment, recovery prediction, and patients’ prioritizing. The pandemic also triggered telehealth development, as a recent case in Spain shows the effect of using patients’ data for predicting whether a person needs immediate intensive care unit admission. Read more on AI and ML grappling pandemic in our recent post.
Per Subroto Mukherjee, AI and machine learning can hold their role in the fight with the pandemic by finding out coronavirus’s biological secret. The crisis affected not only drug development but also a global supply chain. AI’s power of planning, forecasting, automation, and collaboration can also unleash supply companies’ management.
Such applications as natural language processing and computer vision apply to current initiatives. The US White House, with the help of the AI community, started the process of medical literature mining to understand a coronavirus’s nature. Medical imaging companies are already using CT image processing to detect coronavirus-induced pneumonia.
Machine learning and AI are demonstrating transformative power on the European pharmaceutical and healthcare market. Meanwhile, it is a domain that still needs to find out optimal modus operandi concerning privacy and clarity to all the actors. To meet all the criteria and ensure progress in a current global fight with the pandemic, we should apply the known tools considering the guidelines. Daring to bring positive results in exponential growth using AI and machine learning is real.