Last year, when Open AI introduced to the world ChatGPT-3, it absolutely revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence and changed the lifestyle of millions of people. This generative AI tool can create a broad answer to almost any question and is considered to be one of the best chatbots that have ever been created.
Right now, generative AI is the newest form of artificial intelligence, and it's making a huge impact in every industry, especially in EdTech. However, many companies are presenting their solutions and creating the illusion that generative AI can solve everything. At the same time, many experts are raising concerns regarding the social and employment implications of generative AI, stating that new tools can destabilize our society.
When we are talking about the Education field, there are many different opinions on AI: some teachers have rejected AI in education, having concerns about its impact on the quality of the study process, and other instructors compare the use of chatGPT to the use of calculators in school.
So, let's explore the technology behind the term generative AI.
Generative AI is a type of AI system that can create text, images, or other forms of media in response to various prompts. The most common approach is basically providing the text as an input prompt. For example, Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 respond to textual prompts by producing corresponding text. Such systems definitely have contributed to the popularity of generative AI, and increased interest in the application of such tools in education and other industries.
However, the spectrum of GenAI goes far beyond text-based inputs – generative AI can handle a variety of input types such as image, voice input, etc. In the pictures below, you can see how GenAI works and what are the types of Generative AI based on data:
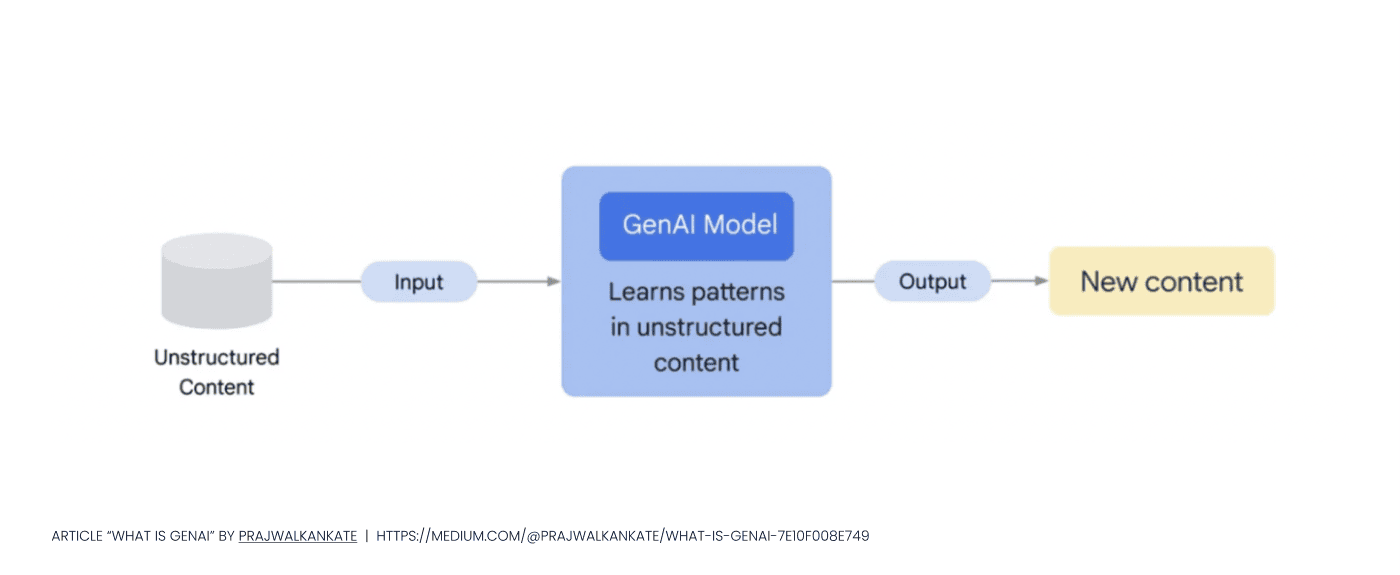
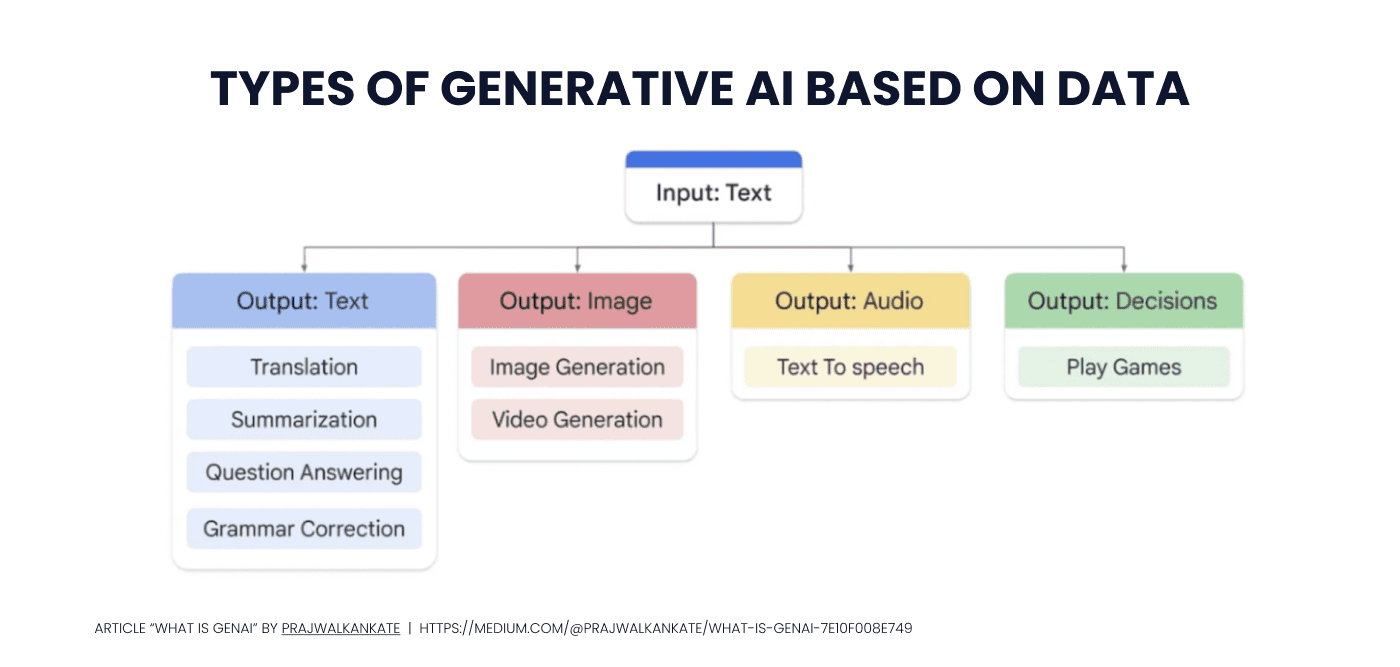
Let us provide you with examples of different types of input and output data:
Well, it is a common-knowledge fact that AI algorithms are trained using human-generated content. And unfortunately, such content can have some flaws, which can lead to imperfections in AI algorithms. Let us show you the main flaws of Generative AI in Education:
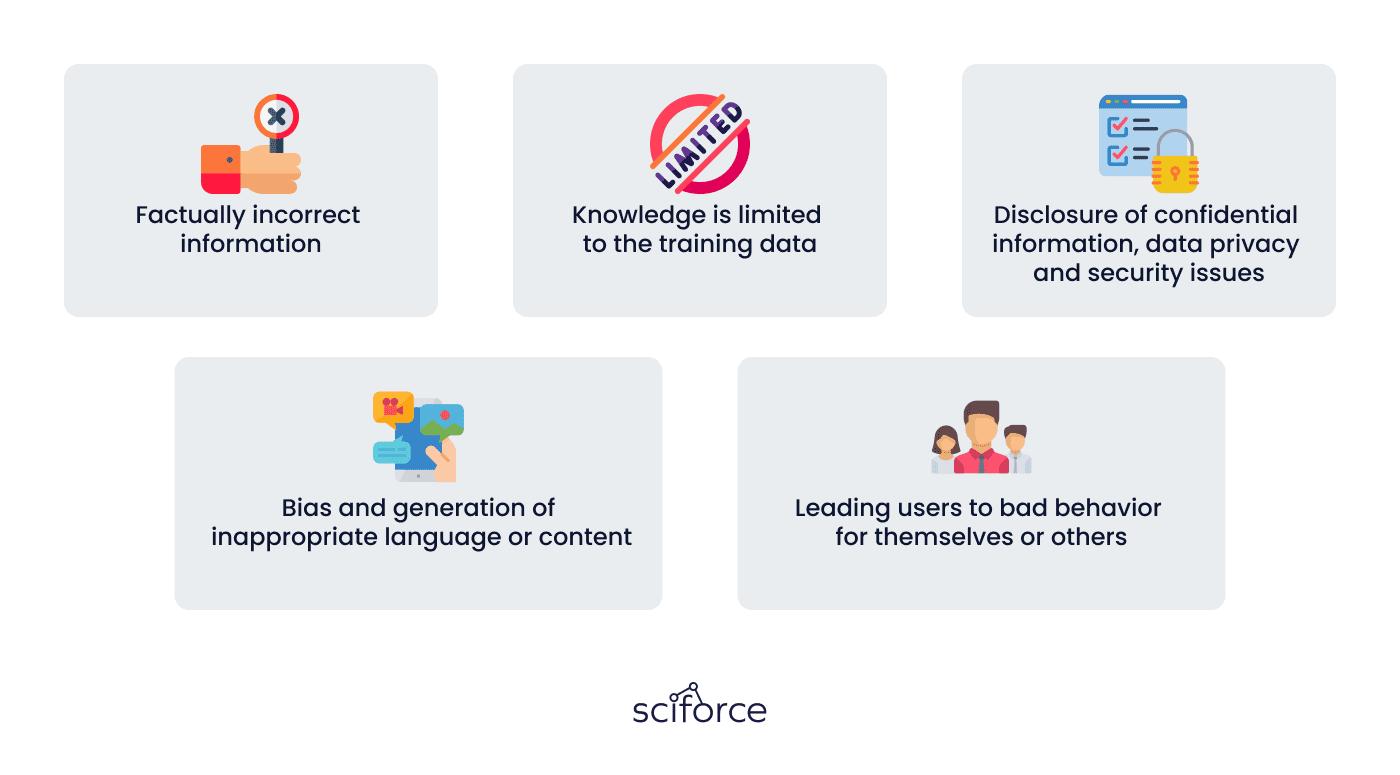
Sometimes it is possible that the LLM system will answer your question with a factually incorrect but well-formulated answer. The thing is that the priority of the model is word sequence generation and not validation of information. This means that users are liable for fact-checking the information, though algorithms may change this soon.
**An effective remedy: **
A few approaches can be used to solve the issue of factually incorrect information that GenAI creates. And the most common and effective ones are post-processing fact-checking and implementation of the feedback system.
Basically, the post-processing fact-check is the process when the model generates an answer, and a separate fact-checking system verifies the information. This system can, for example, cross-reference the generated text with a database of verified facts.
The feedback system enables users to flag incorrect or misleading information. And, afterward, this feedback can be used to improve the future responses of the model.
Without internet access, a standard LLM engine lacks knowledge of unfamiliar topics, resulting in false or no responses.
An effective remedy:
The model can be integrated with a search engine, or users can enhance the generated answers by giving the model additional sources for responses (for example, books or articles). Also, the model can be tuned for any particular case. For example, Open AI has recently published a tutorial on how to customise a model for an application for your particular purposes.
AI in EdTech often requires collecting and analyzing vast amounts of student data. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is crucial to prevent breaches and misuse.
Training data used in LLMs do not include any confidential information like biometrical data, medical personal data, banking data, etc.
However, because of the fact that LLM training requires a large amount of data, the process of content filtering needs to be done automatically, and privacy filtering algorithms can be imperfect. So, it is possible that some sensitive or confidential data can leak.
**An effective remedy: **
Data anonymisation or de-identification can effectively solve that problem. These processes aim to remove personally identifiable information from datasets, allowing for data analysis without compromising privacy. There are many effective types of data anonymization methods, like deletion of direct and indirect identifiers, pseudonymization/tokenization, data masking, introducing statistical noise, data aggregation, and synthetic data usage.
Even in the case when training data was sorted out, and inappropriate content was filtered before training, LLM can still generate harmful content. Some conversational AI models like ChatGPT use training techniques involving humans to prevent certain types of content from being generated, but it still happens occasionally. Thus, there is a need in the development of appropriate content filters to avoid harmful and inappropriate content generation.
**An effective remedy: **
The problem with AI bias can be solved at early stages by testing data and algorithms and using best practices to collect the data. To address the issue of bias in AI systems, we usually start by thoroughly understanding the algorithm and data to assess high-risk areas of unfairness, examining the training dataset for representativeness, and conducting subpopulation analysis. Also, it is important to monitor the model over time and establish a comprehensive debiasing strategy that encompasses technical, operational, and organizational actions.
Also, one more effective way to fix this issue is using human feedback during fine-tuning. Some examples of using such an approach are InstructGPT and Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF).

Even though the implementation of GenAI in Edtech might bring some challenges, the ability to change how students interact with learning resources overcomes these drawbacks. It is important to understand that any technology has its imperfections, however, as we demonstrated earlier, such difficulties can be solved.
Thus, we all should bear in mind that AI in EdTech is not only about intelligent responses, it's about creating a secure and unbiased educational environment for every student.
Although, at this moment, genAI has some flaws, advantages are overtaking the disadvantages in many cases.
For example, one of the biggest strengths of LLM models is their capacity to produce grammatically and syntactically accurate language when given existing text. LLM models acquire this skill through training with properly written English texts. During output generation, each word is chosen based on its likelihood, considering the previous context and the model's learned knowledge, which heavily relies on the grammar and syntax from the training data.
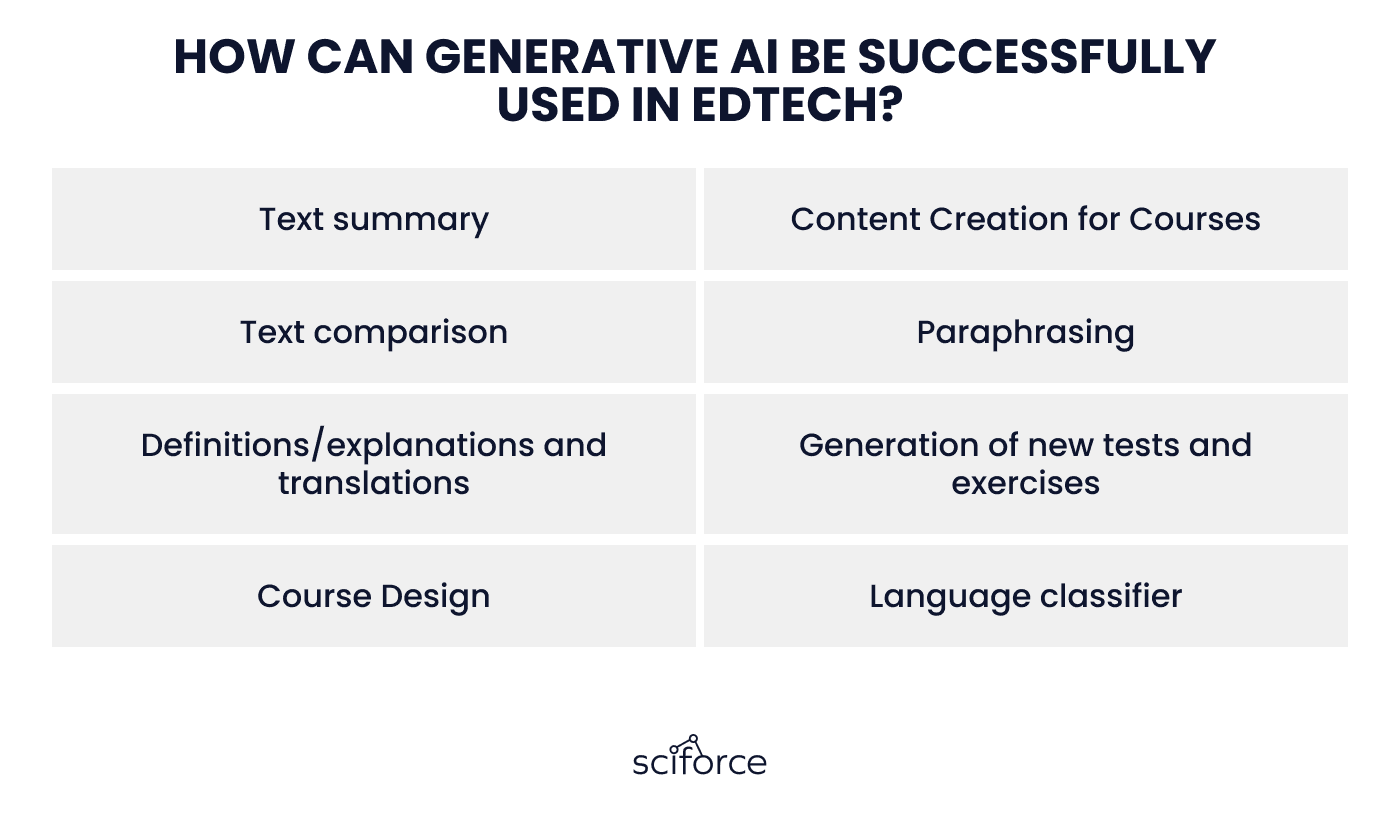
Such a capacity allows people to use generative AI in EdTech in the following cases:
Users can ask LLMs to summarise long texts while keeping the meaning and main details. This is a very helpful way of extracting important information from complex texts. Also, LLM can simplify information that is too hard to understand.
Generative AI can help in creating course materials. For example, quizzes, exercises, explanations, tests, and summaries, benefit teachers who need diverse content.
LLM models are capable of comparing two texts and detecting their differences and similarities. Researchers can ask AI to analyze two research papers and highlight variations in conclusions, and approaches or set any other relevant criteria.
LLMs can be used to improve clarity and correct mistakes in any trained language. Moreover, besides the rephrasing, we can ask AI to compare both versions of the text and provide explanations for the changes made. This allows students to gain insights and learn from their own mistakes.
Generative AI has a great capability for the translation and explanation of terms. In many cases, AI can be better than regular dictionaries and translators as it takes into account the context of the words. Also, it can cover a lot of idioms and phrases in English.
Based on the description, we can use LLMs to create different exercises and tests for students. Here everything depends on the desired type of exercise and how well-detailed the description is. You can even ask the tool you are using to provide an explanation for the correct answers to the exercise or test. However, we must remember that the LLM's output may not be perfect, and corrections might be needed.
GenAI tools can become extremely useful for designing and structuring course materials like syllabi, lesson plans, and individual assignments. They can also personalize the content of the course to match individual students' knowledge gaps, skills, and learning styles by practicing problematic areas and creating interactive exercises.
LLM models can be used as general-purpose language classifiers. This means that they can classify input text into a variety of predefined categories. For example, we can ask it to tell us what language a text is written in, the emotion/sentiment of the text, its writing tone, etc.
This list does not fully cover all possible applications of generative AI in education. Some of these use cases may not be suitable for all types of data and tasks. To achieve the best results, we suggest you get insights from successful implementations, find effective strategies, and tailor them to your specific case.
However, to ensure the efficiency of generative AI applications, lecturers should ensure that the following principles for the effective and ethical use of AI are well-explained to students.
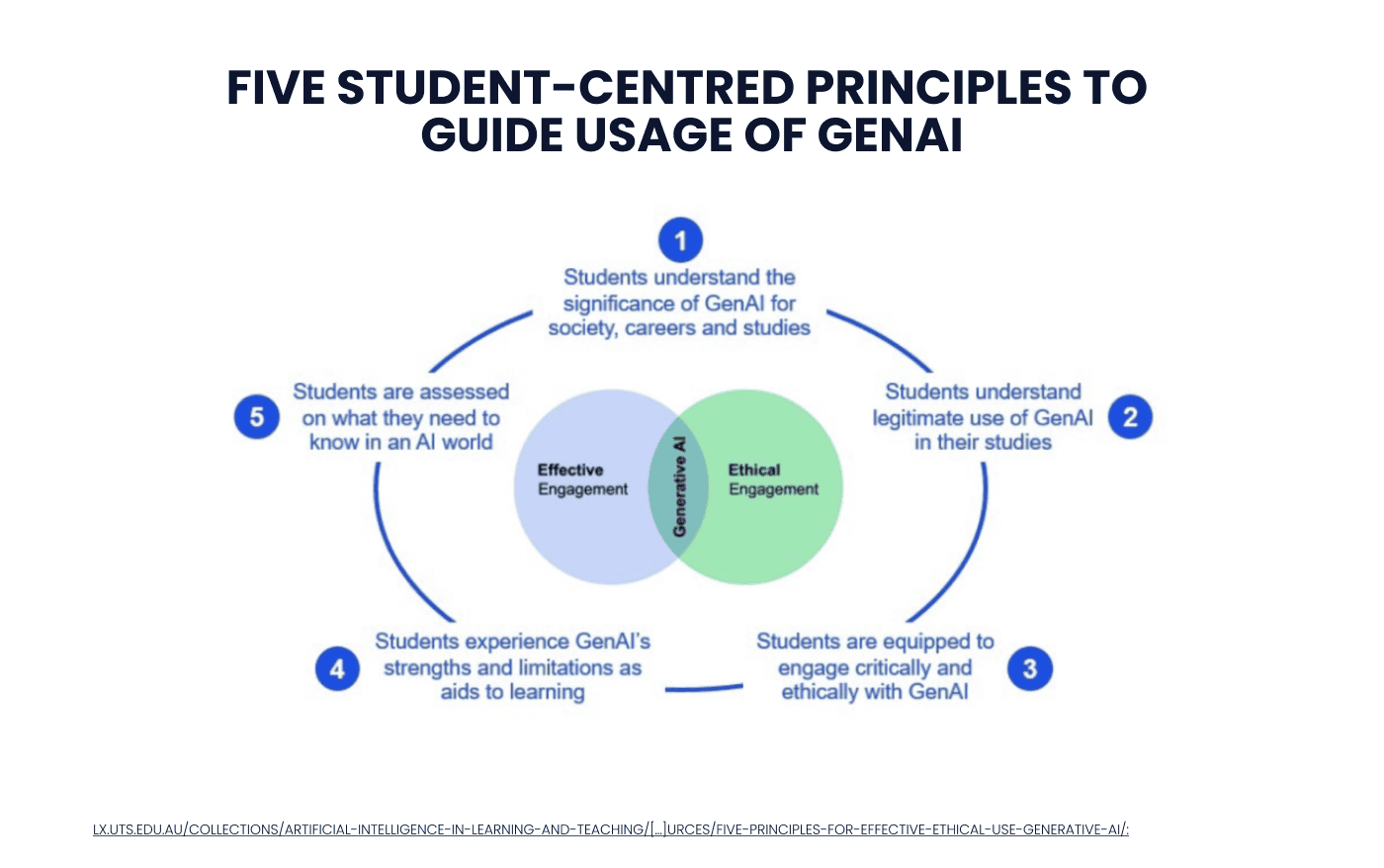
Even though AI is gaining popularity everywhere, it's crucial to understand not only the advantages of its usage but also the limitations and potential risks. By using genAI's language capabilities, the EdTech sector can truly benefit from improved content generation, summarization, translation, and explanations. However, we must be extremely cautious because genAI might produce incorrect or nonsensical information. In order to optimize the benefits of this technology, integrating generative AI with expert systems can ensure the delivery of accurate and reliable knowledge, which will definitely positively change the educational experience for both: students and lecturers.
Our conversation doesn't end here. We are truly eager to learn from you too! How are you integrating GenAI into your educational responsibilities? Share your insights and experiences in the comments below!