Voice biometry is changing the way businesses operate by using distinctive features of a person's voice, like pitch and rhythm, to confirm their identity. This technology, a central part of Voice AI, turns these voice characteristics into digital "voiceprints" that are used for secure authentication. Unlike traditional methods such as fingerprint or facial recognition, voice biometry can be used remotely with just standard microphones, making it both practical and non-intrusive.
This technology enhances security using advanced algorithms that block fraudulent attempts, making it a popular choice in various sectors requiring reliable and user-friendly authentication solutions, such as finance, healthcare, and customer support.
The voice biometric market, valued at $1.261 billion in 2021, is expected to grow significantly, with a projected annual growth rate of 21.7%. By 2026, the market is anticipated to exceed $3.9 billion. Voice recognition is a valuable method capable of improving the security and customer service and offering rich personalization experience. Today we’ll explore, how it works and take a look on use cases in different areas of business
Voice is produced when humans push the air from the lungs through the vocal cords, causing them to vibrate. Vibrations resonate in the nasal and oral cavity, releasing the sounds to the world.
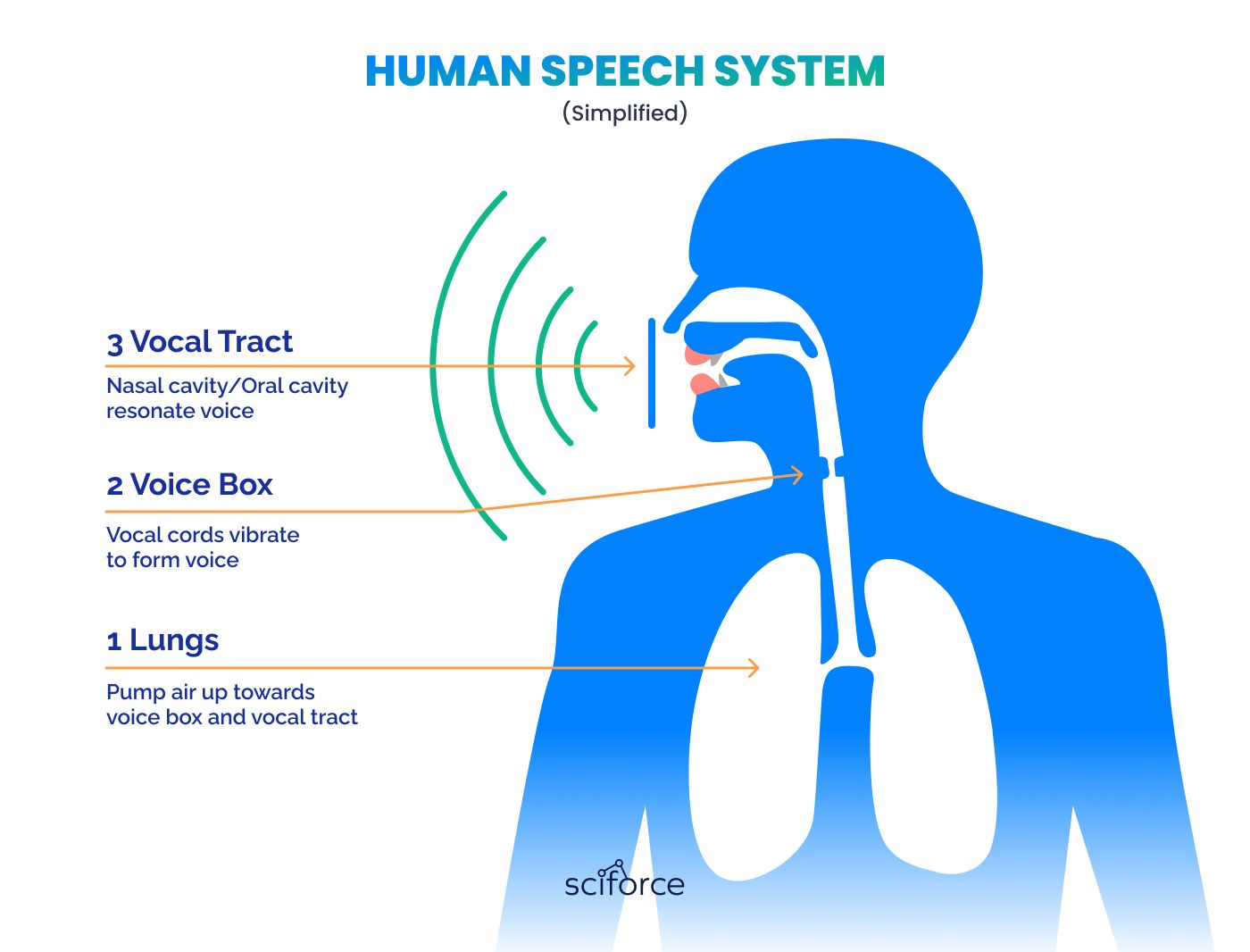
Each human's voice has unique characteristics, such as pitch, tone, and rhythm, shaped by the anatomy of their vocal organs. This makes the voice as unique as fingerprints, faces, or eyes. Voice recognition identifies individuals by analyzing the unique characteristics of their voice. This involves two key stages:
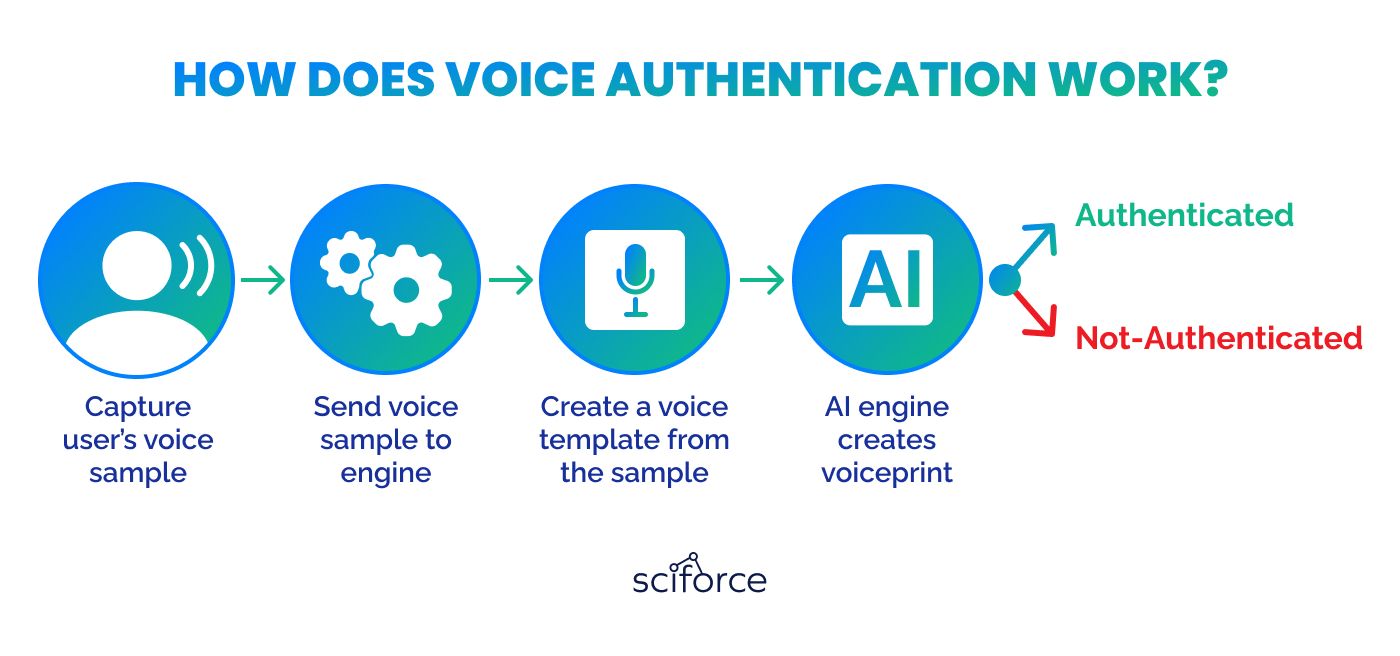
This is the first step in setting up voice biometrics, where a person’s voice is captured and converted into a digital model called a "voiceprint." This process includes several important stages:
Acoustic Analysis
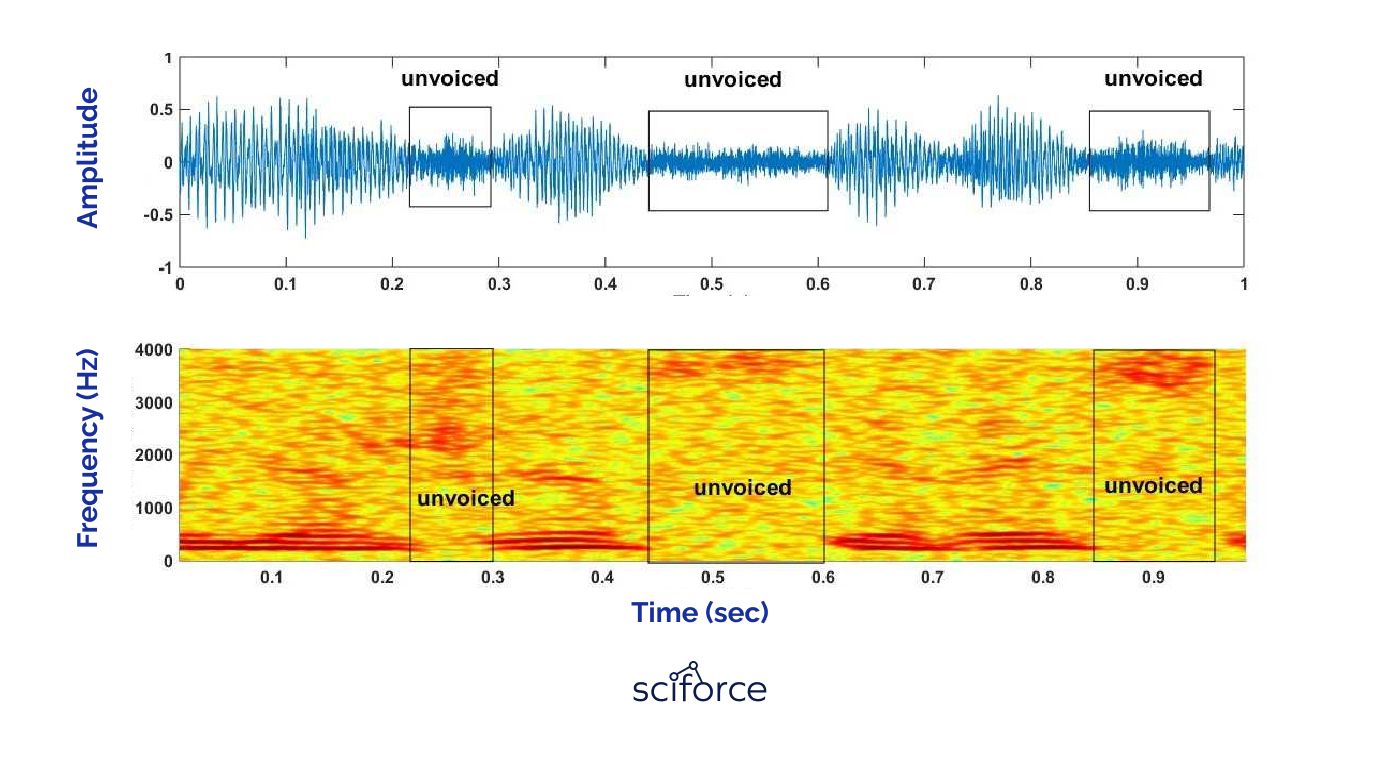
This stage involves analyzing the voice sample as an acoustic wave. Technicians use a waveform or a spectrogram to visualize the voice. Waveform displays the amplitude of voice, featuring the loudness, while spectrogram reflects the frequency, representing them in color or grayscale shading.
Mathematical Modeling
After analyzing the voice, its unique characteristics are transformed into numerical values through mathematical modeling. This step uses statistical and artificial intelligence methods to create a precise numerical representation of the voice, known as a voiceprint.
Active & Passive Extraction
Active Voiceprint Extraction requires the person to actively participate by repeating specific phrases. It’s used in systems that need very accurate voiceprints.
Passive Voiceprint Extraction captures voice data naturally during regular conversation, like during a customer service call. It doesn’t require any specific effort from the user, making it more convenient and less intrusive.
The choice between active and passive extraction depends on the needs of the system, such as the level of security required and how intrusive the process can be for users.
Voiceprints are securely saved in a database, and each is stored in a unique format set by the biometrics provider. This special format ensures that no one can recreate the original speech from the voiceprint, protecting the speaker's privacy.
Voiceprint Comparison
When a new voice sample is provided, it is quickly compared to the stored voiceprints to check for a match, which is crucial for verifying identities.
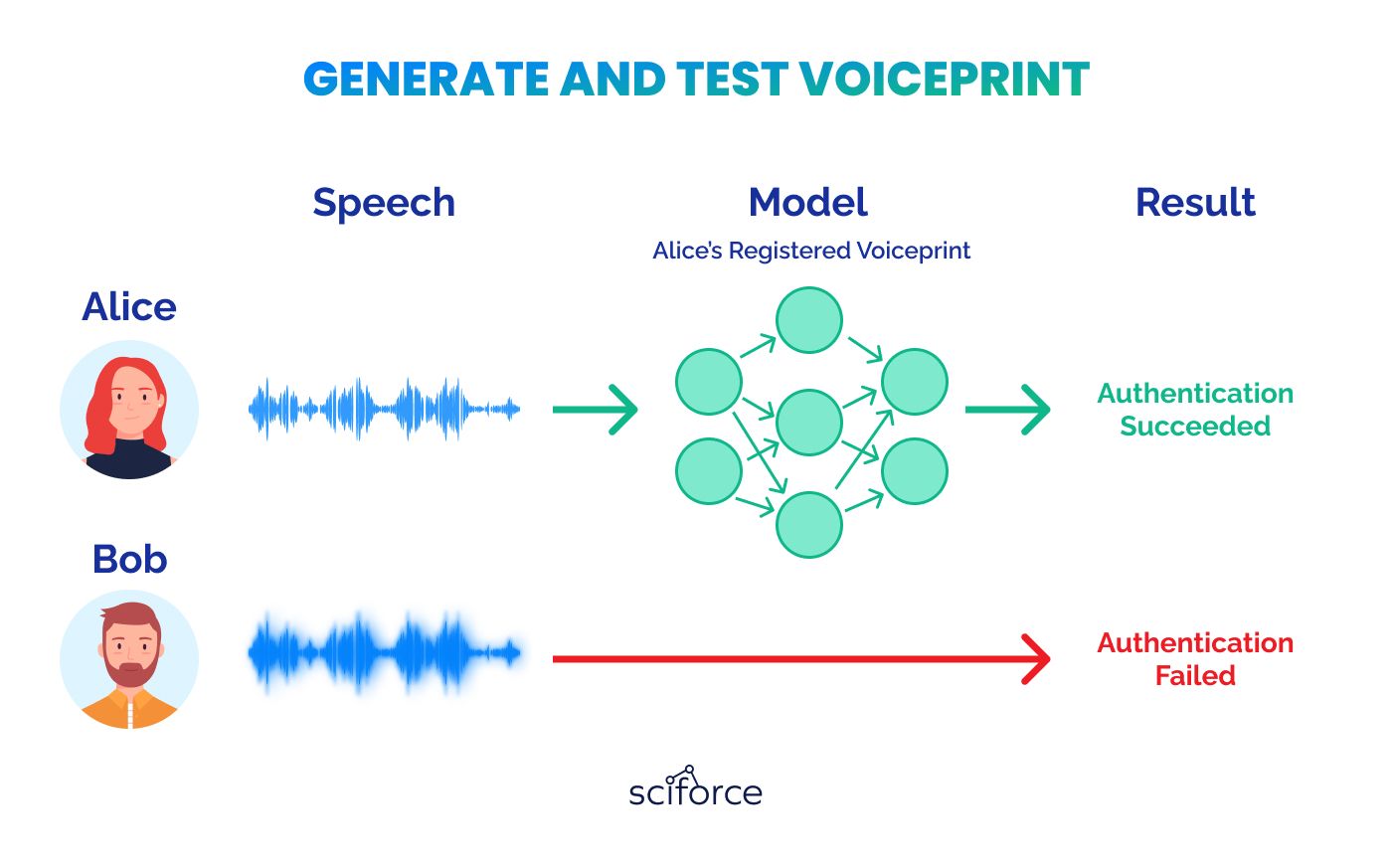
This comparison can happen in a few ways:
The authentication process in voice biometrics determines if access is granted by comparing a submitted voice sample against stored voiceprints. A score is calculated based on this comparison; if the score meets or exceeds the predetermined threshold, access is granted, confirming the user’s identity. If the score is too low, access is denied, signaling that the identity could not be verified.
Voice biometrics also features robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access. The complexity of human voice characteristics makes accurate duplication difficult, providing a natural layer of security. Additionally, the system employs advanced algorithms that detect and thwart spoofing attempts, including synthetic voices and recordings.
Voice biometrics is a secure and effective alternative to traditional methods like passwords and PINs, which are becoming more vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. At the same time, voice biometrics offers plenty of other opportunities, besides secure authentication, and now we are going to explore them.
Voice biometrics customer service representatives to authenticate callers just by their voice, eliminating the need for traditional security questions. By quickly authenticating customers through their unique voiceprints, call centers can reduce the average call handling time by 25-45 seconds.
Barclays Bank has improved its customer service operations by implementing voice biometrics, which identifies customers within just 20 seconds — reducing average call handling times by 15%. Barclays reports 93% of customer approval rating and 60% less complaints regarding call duration.
Businesses are using voice recognition technology to enhance customer interactions by quickly accessing profiles and past interactions through voice identification. This allows them to personalize recommendations and adjust services based on individual preferences and behavior:
Amazon uses Voice Profiles to create personalized user experience on Alexa devices. Once set up, Alexa can identify different family members, customize interactions based on their preferences:
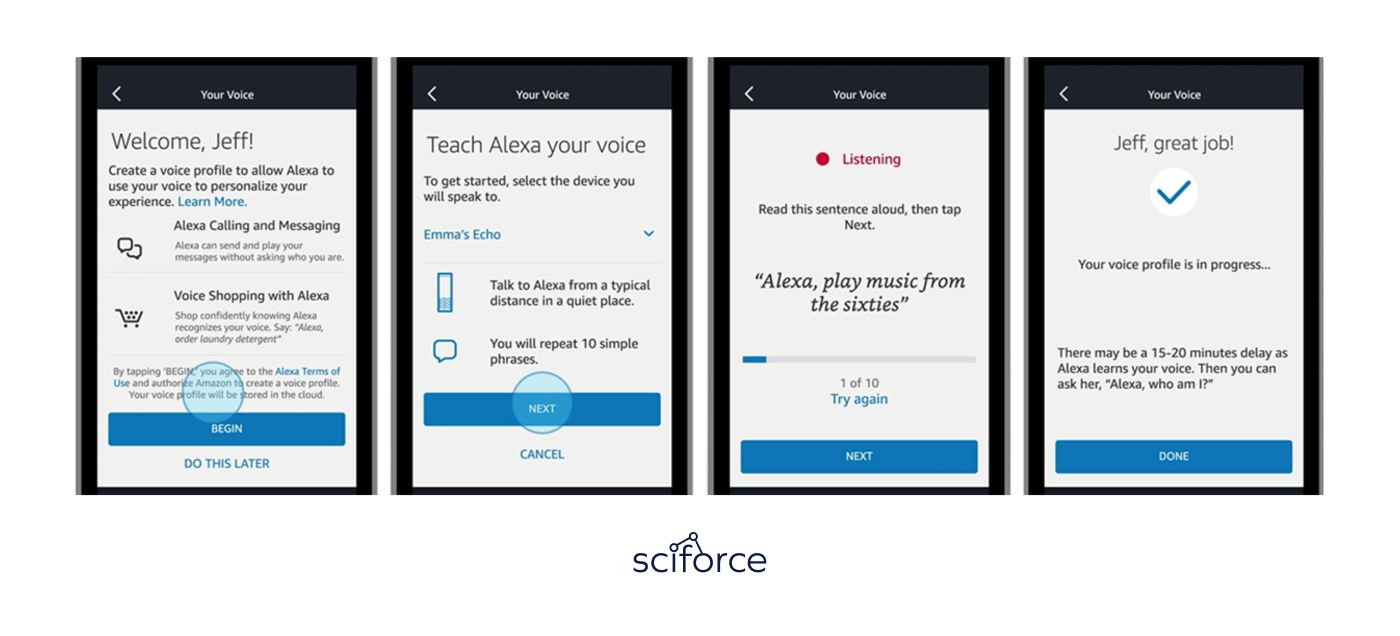
This creates a feeling, like each family member uses their own Alexa device, greatly improving customer experience.
Voice biometrics significantly improves accessibility for individuals with physical or visual impairments by providing a simple, spoken method for authentication. Instead of needing to type passwords or interact with touchscreens, users can verify their identity through their voice.
Google Home devices support voice commands to control various smart home features like lights, thermostats, and locks. For people with disabilities, this functionality allows them to manage their environment easily and independently, enhancing their ability to live comfortably without needing physical switches or controls.
Analyzing unique voice features, speech biometrics is an effective protection from fraud. Despite concerns about audio deep fakes, they are still unable to replicate natural pitch, tone, and speaking style, in real-time interaction. Combining voice recognition with multi-factor authentication offers far greater security than traditional systems.
HSBC UK's Voice ID, has protected nearly £249 million from telephone fraud over the past year, reducing fraud attempts by 50%. As digital and telephone banking usage grows, over 2.8 million customers have adopted Voice ID for a more secure, quick, and convenient banking experience.
Voice biometrics technology integrates smoothly across various customer service channels, including call centers, websites, and mobile apps, enhancing security and consistency. This allows businesses to offer uniform service quality across all touchpoints.
HSBC's voice biometrics system that we’ve already mentioned is a perfect example of multi-channel customer interaction both in online banking portal and in customer support operations.
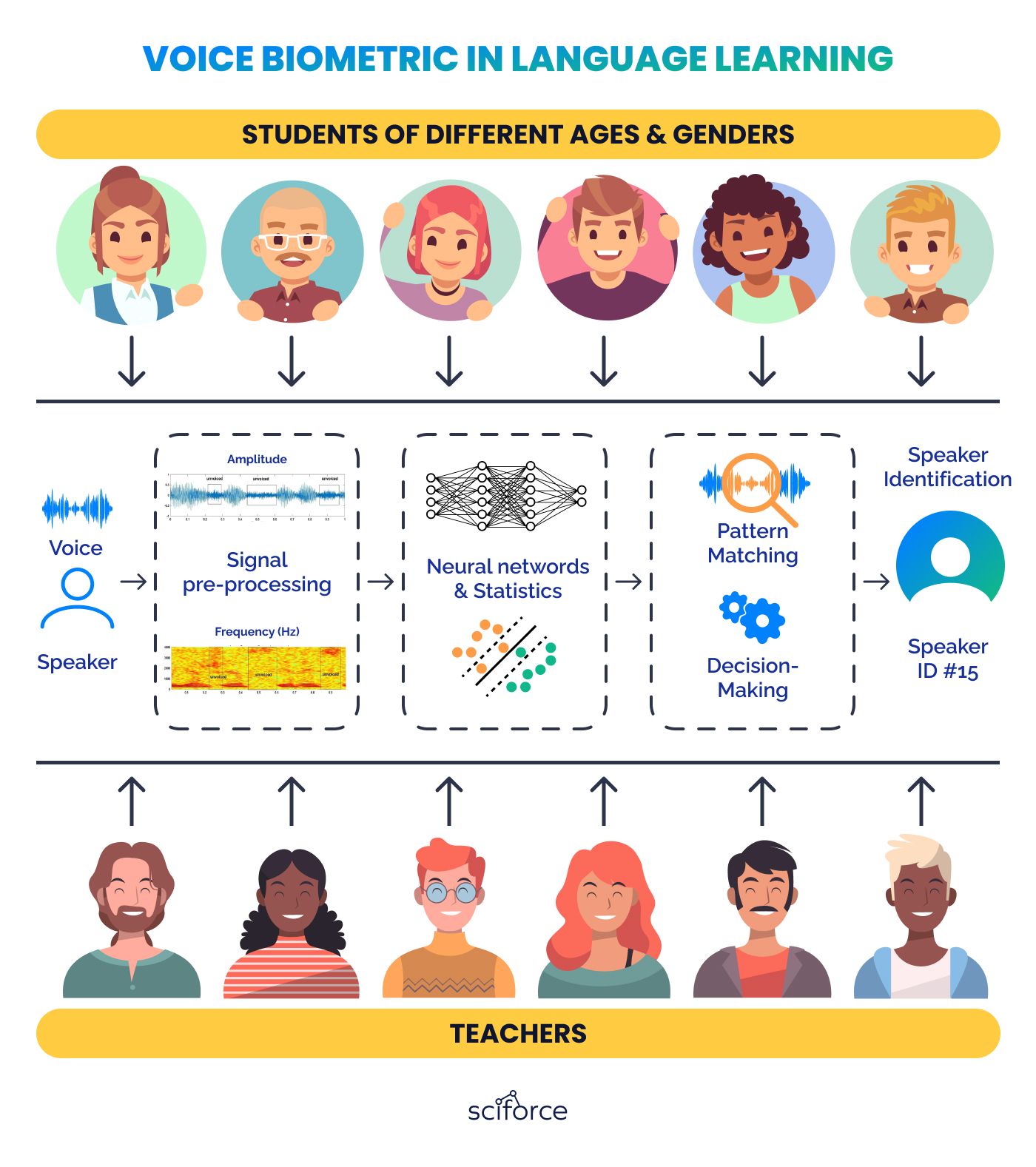
Voice biometrics can also be used in education for personalization, attendance tracking, verifying students during the exams, and removing physical barriers for impaired students. In language learning, it can give real-time feedback on pronunciation and fluency. Voice recognition systems can analyze spoken language exercises, offering instant corrections and tips.
Gender \ Age Classification It sorts voices into male and female categories based on the physical differences in vocal structures. This helps customize language learning methods to match the distinct tones of each gender. Moreover, it groups voices by age, like adults, teenagers, and children, enabling more customized learning methods that match the developmental stages and language patterns of each age group.
Teacher \ Student Classification The system stores and identifies the unique voice patterns of educators, making it easy to access their teaching materials separately from student recordings. Individual student voiceprints are recognized as well for personalized feedback and progress tracking.
A prominent North-American e-Learning technology company, supporting e-learning across over 100 languages, aimed to improve their language learning products by incorporating advanced speech recognition techniques. Our goal was to create a solution for analyzing and providing instant feedback for learner's pronunciation. The challenge was to create a system that could handle diverse accents, dialects, and noisy environments, making language learning more accessible and effective.
Main Challenges
Solution
The language learning platform supports various types of exercises, including writing ones, guessing games, and pronunciation training. This module focuses on providing precise, unsupervised pronunciation training, helping the students to refine their pronunciation skills autonomously.
How It Works
When a student speaks, the system displays a visual waveform of their speech. This points out errors by highlighting incorrect words, syllables, or phonemes and offers the correct pronunciation. It also presents alternative pronunciations, providing learners with a broad understanding of different speaking styles.
The pronunciation evaluation module uses artificial neural networks and deep learning to analyze speech patterns, while machine learning and statistical methods identify common errors. Decision trees analyze speech patterns against set linguistic rules to determine pronunciation accuracy, identify errors, and suggest corrections.
Implementation
The development team upgraded from traditional MATLAB-based ASR models to a more sophisticated, TensorFlow-powered end-to-end ASR system. This new system uses the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to convert sounds directly into phonetic symbols, efficiently supporting multiple languages within a single system. Key features include:
Conclusion
Analyzing unique voice characteristics offers endless possibilities in various business areas. More secure than traditional passwords, voice recognition can safeguard customers’ money and sensitive information, like health records. Quick processing of client support requests, easy and non-intrusive authentication will both please the customers and make business more efficient. Voice recognition can even become a key selling feature in your product – like training pronunciation of language learners.
SciForce has rich experience in speech processing and voice recognition. Contact us to explore new opportunities for your business.